

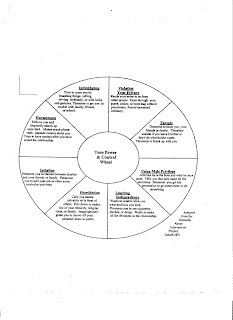

Notes:
Abuse: any form of misuse or mistreatment of a person
Emotional abuse: nonphysical mistreatment of a person- can destroy a person’s sense of worth. Examples include verbal abuse such as name calling, insults or threats, criticism and put downs, controlling how a person dresses or acts, damaging or destroying property, demanding to know a person’s whereabouts at all times.
Physical abuse: intentional use of physical force as punishment or to exert power, control and fear over another. Leaves a mark the next day. Examples include hitting, kicking, scratching, biting, punching, using objects to physically hurt someone.
Sexual abuse: includes unwanted kissing to inappropriate touching to sexual intercourse, rape.
Cycle of Violence:
Tension building stage- precedes the violence. The abusive partner blames, criticizes, controls, threatens or makes fun of the other person.
Tension building stage- precedes the violence. The abusive partner blames, criticizes, controls, threatens or makes fun of the other person.
Explosion stage- when violence erupts. It can be emotional, physical, and/or sexual.








